Skin Infections
Basics
Learn More
See, Play and Learn
Research
Resources
For You
Summary
What are skin infections?
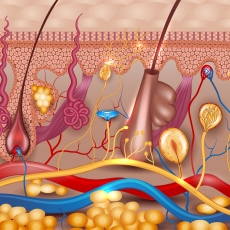
Your skin is your body's largest organ. It has many different functions, including covering and protecting your body. It helps keep germs out. But sometimes the germs can cause a skin infection. This often happens when there is a break, cut, or wound on your skin. It can also happen when your immune system is weakened, because of another disease or a medical treatment.
Some skin infections cover a small area on the top of your skin. Other infections can go deep into your skin or spread to a larger area.
What causes skin infections?
Skin infections are caused by different kinds of germs. For example,
- Bacteria cause cellulitis, impetigo, and staphylococcal (staph) infections
- Viruses cause shingles, warts, and herpes simplex
- Fungi cause athlete's foot and yeast infections
- Parasites cause body lice, head lice, and scabies
Who is at risk for skin infections?
You are at a higher risk for a skin infection if you
- Have poor circulation
- Have diabetes
- Are older
- Have an immune system disease, such as HIV/AIDS
- Have a weakened immune system because of chemotherapy or other medicines that suppress your immune system
- Have to stay in one position for a long time, such as if you are sick and have to stay in bed for a long time or you are paralyzed
- Are malnourished
- Have excessive skinfolds, which can happen if you have obesity
What are the symptoms of skin infections?
The symptoms depend on the type of infection. Some symptoms that are common to many skin infections include rashes, swelling, redness, pain, pus, and itching.
How are skin infections diagnosed?
To diagnose a skin infection, health care providers will do a physical exam and ask about your symptoms. You may have lab tests, such as a skin culture. This is a test to identify what type of infection you have, using a sample from your skin. Your provider may take the sample by swabbing or scraping your skin, or removing a small piece of skin (biopsy). Sometimes providers use other tests, such as blood tests.
How are skin infections treated?
The treatment depends on the type of infection and how serious it is. Some infections will go away on their own. When you do need treatment, it may include a cream or lotion to put on the skin. Other possible treatments include medicines and a procedure to drain pus.
Diagnosis and Tests
- Fungal Tests (American Association for Clinical Chemistry)
-
Skin Biopsy
 (National Library of Medicine)
Also in Spanish
(National Library of Medicine)
Also in Spanish
- Skin Rashes and Other Problems (American Academy of Family Physicians) Also in Spanish
- Wood's Lamp Examination (Logical Images)
Related Issues
- Skin Complications (American Diabetes Association) Also in Spanish
- Swimming Pools and Molluscum Contagiosum (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
Specifics
- Blastomycosis (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Boils (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Boils and Carbuncles (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research) Also in Spanish
- Cutaneous Larva Migrans (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Erysipelas (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Erythema Nodosum (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Intertrigo (American Academy of Family Physicians) Also in Spanish
- Molluscum Contagiosum (American Academy of Dermatology)
- Molluscum Contagiosum (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Rare Disease, Especially for the Healthy (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) Also in Spanish
- Onchocerciasis (River Blindness) FAQs (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Sporotrichosis (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Tinea Versicolor (American Academy of Dermatology)
- Tinea Versicolor (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
Images
- Boils (Furunculosis) (Logical Images)
- Erythema Nodosum (Logical Images)
- Erythrasma (Logical Images)
- Intertrigo (Logical Images)
- Molluscum Contagiosum (Logical Images)
- Tinea Versicolor (Logical Images)
Clinical Trials
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Molluscum Contagiosum
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Skin Diseases, Infectious
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
Journal Articles References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
Find an Expert
- American Academy of Dermatology
- Find a Dermatologist (American Academy of Dermatology)
-
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases

Children
- Molluscum Contagiosum (American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus)
- Molluscum Contagiosum (For Parents) (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
Teenagers
- Cuts, Scratches, and Scrapes (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
- Molluscum Contagiosum (Children's Hospital Boston) Also in Spanish
Patient Handouts
- Blastomycosis (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Boils (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Candida infection of the skin (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Carbuncle (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Donovanosis (granuloma inguinale) (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Ecthyma (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Erysipelas (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Molluscum contagiosum (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Necrotizing soft tissue infection (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
